Difference between revisions of "Engage 10"
m (→Raspberry Pi Config) |
(→Raspberry Pi Config: Tested with buster release) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
These devices were intended to be WUSB touchscreens. | These devices were intended to be WUSB touchscreens. | ||
| − | They include an internal WUSB device dongle, an internal USB hub, a USB | + | They include an internal WUSB device dongle, an internal USB hub, a USB displaylink video chip feeding VGA to an LCD driver, and a USB HID touchscreen. |
The LCD seems to be 1024 x 600 native resolution. | The LCD seems to be 1024 x 600 native resolution. | ||
| + | They will do 1024 x 768, but it does not look as good. | ||
The box should include the display, an external WUSB host dongle, a 12 volt (usually 3 amp) power supply and a USB A to USB A cable. | The box should include the display, an external WUSB host dongle, a 12 volt (usually 3 amp) power supply and a USB A to USB A cable. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
The pairing process seems to be tricky... | The pairing process seems to be tricky... | ||
| − | The | + | The displaylink chip is a DL-125, old and well supported. |
* The current raspbian image has a kernel module driver for it. | * The current raspbian image has a kernel module driver for it. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
* Current Ubuntu distrubtions seem to hot plug the display and bring up GUI to configure it, but guess the resolution badly. | * Current Ubuntu distrubtions seem to hot plug the display and bring up GUI to configure it, but guess the resolution badly. | ||
| − | * Current Debian distrubtions seem to have the driver | + | * Current Debian distrubtions seem to have the driver, but they do not bring up any GUI to configure it. |
| − | * Windows XP works after installing a | + | * Windows XP works after installing a displaylink driver, I have not tried newer versions on the metal, and had trouble with 7 on a VM. |
In general, plugging the display into a linux computer should cause a new fb device to show up in /dev/ and you can then do what you like with it, including x11. | In general, plugging the display into a linux computer should cause a new fb device to show up in /dev/ and you can then do what you like with it, including x11. | ||
| − | A solid green screen is generally a | + | A solid green screen is generally a sign that the driver is working. |
== Wired USB Connection == | == Wired USB Connection == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
Instead, I have been using the included USB cable. | Instead, I have been using the included USB cable. | ||
| − | + | On a very few devices the external USB port will work. | |
| − | + | In general, however, you will need to open the case, remove the WUSB module and plug the cable into the internal USB port. | |
| − | + | You can use a round file or similar tool to make a notch in the case for the cable. | |
| − | + | If lsusb lists a displaylink device, USB is working. | |
| − | + | A solid green screen means the linux framebuffer driver is working. | |
| − | + | == Wireless USB (WUSB) Connection == | |
| + | Initial study of the removed chip from the base station indicates it's a WISair chipset. According to Linux-Usb, they are not actually compliant with the 1.0 spec of WUSB, but there seems to be workarounds. source: [https://www.spinics.net/lists/linux-usb/msg44020.html link Linux-USB mailing list] | ||
| − | + | Output of dmesg when the plastic-coated dongle is plugged in: | |
| + | |||
| + | <pre>[ 432.176018] usb 3-1: new high-speed USB device number 9 using sw-ehci | ||
| + | [ 432.338051] usb 3-1: New USB device found, idVendor=13cf, idProduct=1200 | ||
| + | [ 432.350885] usb 3-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=2, Product=1, SerialNumber=3 | ||
| + | [ 432.361752] usb 3-1: Product: Wireless USB Dongle | ||
| + | [ 432.369034] usb 3-1: Manufacturer: | ||
| + | [ 432.375874] usb 3-1: SerialNumber: 123456789</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output of dmesg when the internally removed dongle is plugged in: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>[ 1499.735961] The port change to OHCI now! | ||
| + | [ 1500.038747] usb 4-1: new full-speed USB device number 2 using sw-ohci | ||
| + | [ 1500.237326] usb 4-1: New USB device found, idVendor=13cf, idProduct=0611 | ||
| + | [ 1500.250176] usb 4-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=2, Product=1, SerialNumber=3 | ||
| + | [ 1500.261018] usb 4-1: Product: Wireless USB Dongle | ||
| + | [ 1500.268292] usb 4-1: Manufacturer: | ||
| + | [ 1500.275090] usb 4-1: SerialNumber: 123456789</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (That serial number looks awwwwfully suspect....) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | idVendor of 13cf does also show a Wisair, however that idProduct isn't known yet. This should be solved by simply binding the device to the appropriate driver, heeding caution to load the modules in the link above in the prescribed order. Follow how to do that [http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/134878/make-linux-load-specific-driver-for-given-device-realtek-nic link Here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This seems to be the best document on how to use the WUSB subsystem: [https://www.kernel.org/doc/ols/2007/ols2007v2-pages-127-134.pdf link PDF]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Long story short, you have to match the channels on the sending and receiving end. Once you match channels, then the devices over the WUSB enumerate on your local machine as /sys/bus/uwb/devices/uwb0/ (assuming your device is uwb0). | ||
| + | |||
| + | As I understand, you: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>echo 13 0 > /sys/class/uwb_rc/uwb0/beacon</pre> | ||
| + | The 13 is the channel number. You'll have to manually change to find other connections *listening*. | ||
== Raspberry Pi Config == | == Raspberry Pi Config == | ||
| − | To configure raspbian to use the display create /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/60- | + | Starting with the 2017-02-27 release raspbian uses the libinput driver instead of the evdev driver. If you need to use an old image or evdev for some reason you can find what you need in the history of this page. The following has been tested up through the 2020-02-13 image. |
| + | |||
| + | You need to edit 2 new files to get standard raspbian displaying and touching. If you are doing a fresh install you can write the image to the card and then mount the card and add the files before you ever put the card in the pi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To configure raspbian to use the display create /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/60-USB_TouchScreen.conf with the following text: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 54: | Line 91: | ||
Section "Monitor" | Section "Monitor" | ||
Identifier "displaylink monitor" | Identifier "displaylink monitor" | ||
| + | DisplaySize 221 129 | ||
| + | Modeline "1024x600_60.00" 49.00 1024 1149 1245 1312 600 601 611 624 -hsync +vsync | ||
| + | Option "DPMS" "off" | ||
EndSection | EndSection | ||
| Line 63: | Line 103: | ||
SubSection "Display" | SubSection "Display" | ||
Depth 16 | Depth 16 | ||
| − | Modes " | + | Modes "1024x600_60.00" |
EndSubSection | EndSubSection | ||
EndSection | EndSection | ||
| + | |||
| + | Section "InputClass" | ||
| + | Identifier "TouchCalibration" | ||
| + | MatchProduct "eGalax Inc. USB TouchController" | ||
| + | Driver "libinput" | ||
| + | Option "CalibrationMatrix" "0 1 0 -1 0 1 0 0 1" | ||
| + | EndSection | ||
Section "ServerLayout" | Section "ServerLayout" | ||
| − | Identifier " | + | Identifier "Default Layout" |
| − | Screen 0 "displaylink screen" 0 0 | + | Screen 0 "displaylink screen" 0 0 |
| + | Option "DontVTSwitch" | ||
| + | Option "DontZap" | ||
| + | Option "BlankTime" "0" | ||
| + | Option "NoPM" | ||
EndSection | EndSection | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
You might want to enable SSH before rebooting, just in case... | You might want to enable SSH before rebooting, just in case... | ||
| − | /dev/fb0 | + | /dev/fb0 seems to always be the HDMI/composite output, displaylink devices start at /dev/fb1, but if you have other framebuffer devices it could get tricky... |
| − | + | To get libinput to actually handle the touch screen events we need a udev rule. (This changes it from a "TABLET" to a "TOUCHSCREEN"...) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Create /etc/udev/rules.d/99-eGalax.rules with the following very shift heavy text: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <pre> | |
| + | ACTION=="add|change", KERNEL=="event[0-9]*", ENV{ID_VENDOR_ID}=="0eef", \ | ||
| + | ENV{ID_MODEL_ID}=="0001", ENV{ID_INPUT_TABLET}="", ENV{ID_INPUT_TOUCHSCREEN}="1" | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | I am still working on a good way to calibrate the touchscreen, it should be possible with the CalibrationMatrix, but it is a little mindbending for me. If you need a really good calibration right now you might try installing evdev and using the old config files... | |
| − | + | == Hacking == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Case === | === Case === | ||
| Line 101: | Line 146: | ||
It is easy to notch the bottom case half to clear a USB cable plugged into the internal port. I used a round file. you can make it a tight fit on the cable or put a cable tie around the cable inside the case to take any tension. | It is easy to notch the bottom case half to clear a USB cable plugged into the internal port. I used a round file. you can make it a tight fit on the cable or put a cable tie around the cable inside the case to take any tension. | ||
| + | |||
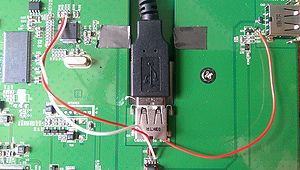
| + | === USB === | ||
| + | The upstream port of the onboard USB hub is connected to U28. | ||
| + | U28 is also connected to the internal USB port (CN1, for the WUSB module) and the external USB port (CN5). | ||
| + | I believe that U28 either connects the WUSB to the external port for pairing, or to the onboard USB hub for normal operation. | ||
| + | Simply removing the WUSB module and plugging the cable into the internal port allows wired USB operation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The onboard USB hub is an NEC 720114, which has 4 downstream ports. | ||
| + | One port goes to the DL chip (U5) and one goes to the touch controller (U15). | ||
| + | The two unused ports are available at R115-116 and R303-304. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Removing R311 (near CN5 pin 1) and connecting pins 1 of the USB ports together provides power on the external port, suitable for a pi. | ||
| + | For higher current needs you might need to get +5v from a different source... | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:USB_hack.jpg|300px|thumb|right|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Turning it into a downstream high speed USB port takes a bit more work. | ||
| + | * Remove R303 and R304 | ||
| + | * Cut the left 2 traces between T1 and U28, being careful not to damage the 2 traces on the right | ||
| + | * Wire the bottom R304 pad to the left T1 pin you just cut away from U28 | ||
| + | * Wire the bottom R303 pad to the right T1 pin you cut away from U28 then connecting the USB side (bottom) R303 pad to CN5 pin 2 and R304 to pin 3. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you need one more port for a keyboard or mouse you can try to wire it directly into R115-116, but without U2 and T1 I have only gotten full speed devices to work, not high speed. | ||
| + | It would be nice to know what U2 is. | ||
=== VGA === | === VGA === | ||
| Line 110: | Line 179: | ||
=== Power === | === Power === | ||
| + | I have quickly tested the input voltage range. The lower limit seems to be around 6.0v and I ran it up to 25v with no smoke. | ||
| + | |||
12 volt current draw is about 550mA for the screen and 800mA for the screen and a pi 2B. | 12 volt current draw is about 550mA for the screen and 800mA for the screen and a pi 2B. | ||
| + | |||
| + | DC in (12v nominal, 12.10 right now) and ground are available at J7. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A slightly lower voltage (11.75v right now) is on J4 and TC4. | ||
| + | This is unregulated, with a 14.35v supply it is 14.00v. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5 volts and ground is available at J3 and TC22. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.3 volts and ground is available at U8 and TC16. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1.25 volts is made by U27. | ||
It would be nice to know how much 5v current is available... | It would be nice to know how much 5v current is available... | ||
| Line 117: | Line 199: | ||
Raspbian seems to try to put the display into some power saving mode. | Raspbian seems to try to put the display into some power saving mode. | ||
It fails to turn off the LCD, but the display glitches when you would expect it to turn the LCD back on. | It fails to turn off the LCD, but the display glitches when you would expect it to turn the LCD back on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Well, I turned off DPMS in xorg.conf, and now the screen blanks. | ||
| + | Different, but not really better... | ||
It would be nice to know exactly what is going on with that... | It would be nice to know exactly what is going on with that... | ||
Latest revision as of 18:54, 15 May 2020
Engage 10 Wireless LCD Model number : W10T200-HWH1WH
These devices were intended to be WUSB touchscreens. They include an internal WUSB device dongle, an internal USB hub, a USB displaylink video chip feeding VGA to an LCD driver, and a USB HID touchscreen.
The LCD seems to be 1024 x 600 native resolution. They will do 1024 x 768, but it does not look as good.
The box should include the display, an external WUSB host dongle, a 12 volt (usually 3 amp) power supply and a USB A to USB A cable. The cable was included just to allow pairing between the WUSB dongles, but it can be used to connect the display directly to the computer.
The pairing process seems to be tricky...
The displaylink chip is a DL-125, old and well supported.
- The current raspbian image has a kernel module driver for it.
- Current Ubuntu distrubtions seem to hot plug the display and bring up GUI to configure it, but guess the resolution badly.
- Current Debian distrubtions seem to have the driver, but they do not bring up any GUI to configure it.
- Windows XP works after installing a displaylink driver, I have not tried newer versions on the metal, and had trouble with 7 on a VM.
In general, plugging the display into a linux computer should cause a new fb device to show up in /dev/ and you can then do what you like with it, including x11. A solid green screen is generally a sign that the driver is working.
Contents |
[edit] Wired USB Connection
I have not actually gotten WUSB to work. I have not tried very hard because it does not seem very useful.
Instead, I have been using the included USB cable. On a very few devices the external USB port will work. In general, however, you will need to open the case, remove the WUSB module and plug the cable into the internal USB port. You can use a round file or similar tool to make a notch in the case for the cable.
If lsusb lists a displaylink device, USB is working.
A solid green screen means the linux framebuffer driver is working.
[edit] Wireless USB (WUSB) Connection
Initial study of the removed chip from the base station indicates it's a WISair chipset. According to Linux-Usb, they are not actually compliant with the 1.0 spec of WUSB, but there seems to be workarounds. source: link Linux-USB mailing list
Output of dmesg when the plastic-coated dongle is plugged in:
[ 432.176018] usb 3-1: new high-speed USB device number 9 using sw-ehci [ 432.338051] usb 3-1: New USB device found, idVendor=13cf, idProduct=1200 [ 432.350885] usb 3-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=2, Product=1, SerialNumber=3 [ 432.361752] usb 3-1: Product: Wireless USB Dongle [ 432.369034] usb 3-1: Manufacturer: [ 432.375874] usb 3-1: SerialNumber: 123456789
Output of dmesg when the internally removed dongle is plugged in:
[ 1499.735961] The port change to OHCI now! [ 1500.038747] usb 4-1: new full-speed USB device number 2 using sw-ohci [ 1500.237326] usb 4-1: New USB device found, idVendor=13cf, idProduct=0611 [ 1500.250176] usb 4-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=2, Product=1, SerialNumber=3 [ 1500.261018] usb 4-1: Product: Wireless USB Dongle [ 1500.268292] usb 4-1: Manufacturer: [ 1500.275090] usb 4-1: SerialNumber: 123456789
(That serial number looks awwwwfully suspect....)
idVendor of 13cf does also show a Wisair, however that idProduct isn't known yet. This should be solved by simply binding the device to the appropriate driver, heeding caution to load the modules in the link above in the prescribed order. Follow how to do that link Here
This seems to be the best document on how to use the WUSB subsystem: link PDF.
Long story short, you have to match the channels on the sending and receiving end. Once you match channels, then the devices over the WUSB enumerate on your local machine as /sys/bus/uwb/devices/uwb0/ (assuming your device is uwb0).
As I understand, you:
echo 13 0 > /sys/class/uwb_rc/uwb0/beacon
The 13 is the channel number. You'll have to manually change to find other connections *listening*.
[edit] Raspberry Pi Config
Starting with the 2017-02-27 release raspbian uses the libinput driver instead of the evdev driver. If you need to use an old image or evdev for some reason you can find what you need in the history of this page. The following has been tested up through the 2020-02-13 image.
You need to edit 2 new files to get standard raspbian displaying and touching. If you are doing a fresh install you can write the image to the card and then mount the card and add the files before you ever put the card in the pi.
To configure raspbian to use the display create /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/60-USB_TouchScreen.conf with the following text:
Section "Device"
Identifier "displaylink device"
driver "fbdev"
Option "fbdev" "/dev/fb1"
Option "ShadowFB" "off"
EndSection
Section "Monitor"
Identifier "displaylink monitor"
DisplaySize 221 129
Modeline "1024x600_60.00" 49.00 1024 1149 1245 1312 600 601 611 624 -hsync +vsync
Option "DPMS" "off"
EndSection
Section "Screen"
Identifier "displaylink screen"
Device "displaylink device"
Monitor "displaylink monitor"
DefaultDepth 16
SubSection "Display"
Depth 16
Modes "1024x600_60.00"
EndSubSection
EndSection
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "TouchCalibration"
MatchProduct "eGalax Inc. USB TouchController"
Driver "libinput"
Option "CalibrationMatrix" "0 1 0 -1 0 1 0 0 1"
EndSection
Section "ServerLayout"
Identifier "Default Layout"
Screen 0 "displaylink screen" 0 0
Option "DontVTSwitch"
Option "DontZap"
Option "BlankTime" "0"
Option "NoPM"
EndSection
You might want to enable SSH before rebooting, just in case...
/dev/fb0 seems to always be the HDMI/composite output, displaylink devices start at /dev/fb1, but if you have other framebuffer devices it could get tricky...
To get libinput to actually handle the touch screen events we need a udev rule. (This changes it from a "TABLET" to a "TOUCHSCREEN"...)
Create /etc/udev/rules.d/99-eGalax.rules with the following very shift heavy text:
ACTION=="add|change", KERNEL=="event[0-9]*", ENV{ID_VENDOR_ID}=="0eef", \
ENV{ID_MODEL_ID}=="0001", ENV{ID_INPUT_TABLET}="", ENV{ID_INPUT_TOUCHSCREEN}="1"
I am still working on a good way to calibrate the touchscreen, it should be possible with the CalibrationMatrix, but it is a little mindbending for me. If you need a really good calibration right now you might try installing evdev and using the old config files...
[edit] Hacking
[edit] Case
The case comes apart easily. There are screws in the corners and plastic clips holding the bottom of the case to top.
It is easy to notch the bottom case half to clear a USB cable plugged into the internal port. I used a round file. you can make it a tight fit on the cable or put a cable tie around the cable inside the case to take any tension.
[edit] USB
The upstream port of the onboard USB hub is connected to U28. U28 is also connected to the internal USB port (CN1, for the WUSB module) and the external USB port (CN5). I believe that U28 either connects the WUSB to the external port for pairing, or to the onboard USB hub for normal operation. Simply removing the WUSB module and plugging the cable into the internal port allows wired USB operation.
The onboard USB hub is an NEC 720114, which has 4 downstream ports. One port goes to the DL chip (U5) and one goes to the touch controller (U15). The two unused ports are available at R115-116 and R303-304.
Removing R311 (near CN5 pin 1) and connecting pins 1 of the USB ports together provides power on the external port, suitable for a pi. For higher current needs you might need to get +5v from a different source...
Turning it into a downstream high speed USB port takes a bit more work.
- Remove R303 and R304
- Cut the left 2 traces between T1 and U28, being careful not to damage the 2 traces on the right
- Wire the bottom R304 pad to the left T1 pin you just cut away from U28
- Wire the bottom R303 pad to the right T1 pin you cut away from U28 then connecting the USB side (bottom) R303 pad to CN5 pin 2 and R304 to pin 3.
If you need one more port for a keyboard or mouse you can try to wire it directly into R115-116, but without U2 and T1 I have only gotten full speed devices to work, not high speed. It would be nice to know what U2 is.
[edit] VGA
I have cut the traces on the displaylink (left) side of J5 and fed VGA into J5. This has worked briefly a few times, I think I was just having trouble generating acceptable resolutions. I think it has promise.
Interestingly, the ¨Searching¨ icon was still present, so it must come from the RTD2033V chip.
[edit] Power
I have quickly tested the input voltage range. The lower limit seems to be around 6.0v and I ran it up to 25v with no smoke.
12 volt current draw is about 550mA for the screen and 800mA for the screen and a pi 2B.
DC in (12v nominal, 12.10 right now) and ground are available at J7.
A slightly lower voltage (11.75v right now) is on J4 and TC4. This is unregulated, with a 14.35v supply it is 14.00v.
5 volts and ground is available at J3 and TC22.
3.3 volts and ground is available at U8 and TC16.
1.25 volts is made by U27.
It would be nice to know how much 5v current is available...
[edit] Power Saving
Raspbian seems to try to put the display into some power saving mode. It fails to turn off the LCD, but the display glitches when you would expect it to turn the LCD back on.
Well, I turned off DPMS in xorg.conf, and now the screen blanks. Different, but not really better...
It would be nice to know exactly what is going on with that...
[edit] Buttons
It would be nice to figure out how the buttons work. At least 4 of them should come over the USB somehow. I did not see them in /dev/input/ so they might be connected to the displaylink rather than the HID...